HR & COMPLIANCE
1. Meaning
The term compliance is simply meant conformity of any developed standard. It revealed the exposition of disciplines, rules, norms, processes, policies, manuals, conducts, and similar matters pertinent to relevant courses of action. Compliance signifies a suitable and absolute plan to ensure the vision of the business. Business firms are said to be compliant where there is an established process, policies, rules, and regulations in the business setups. Therefore, compliance is an important area of interest for the stakeholder to leverage the business sustainability in a fiercely competitive market. Moreover, compliance becomes a desk of discussion to manage human resources. Compliance is not only adding values in the total process of an organization but also acts as a stimulator for the business entity. Academically the HRM activity is composed of HR core functions and HR support functions. The mainstream HRM process includes recruitment, selection, training, performance appraisal, and compensation. Besides, there are supporting functions such as employee services, employee assistance programs, safety and security, leave and attendance, and other organizational supports. In the last few decades, the scope of HRM functions has gradually been explored through organizational practices.
Related research in the context of Bangladesh has claimed some very important areas and findings in light of mainstream functions (Alam-et al., 2017; Hosain, 2017; Nurul et al., 2019). The objectives of the chapter is to define the meaning, importance, scope, and practices of human resources management compliance (HRC) in the context of Bangladesh. Additionally, this chapter is entailed some limited practices of HRC such as service rule and service policy compliance, maternity benefits compliance, wage compliance, compensation for injury by accident compliance, provident and gratuity fund compliance, health and hygiene compliance, welfare compliance, working hours, leaves and holidays compliance, that extracted from the previous literature review in the context of Bangladesh.
Human resources management compliance stands to ensure the relevant adoption of human resources rules, policies, and processes to manage people. It is the heart of business governance to comply with relevant rules, laws, and acts to apply in the firm. A more specific meaning of HRC can be evolved as the process in hand, complying and conformance, maintaining the code of conducts, given rules and regulations (Tsui et al., 2006; Wald & Winterfeldt, 2012). The HRC influence all types of HR functions such as HRM core functions, support, HRM strategy, and policy. Particularly, HRC is a guiding tool of firms to go by the book in an object of confirming the standards. In a wider sense, HRC has closely connected the legal structure and makes the obligations to the organizations in the adoption of definite HR policies, standard work process (SOP), and support services.
Prior scholars in this field Jensen (2015) stated that HRC is composed of “Direct employment-related external regulations” namely the employment regulations, the law of workplace diversity and discrimination, the law of occupational health and safety, income and compensation security. And all regulations are influenced by the state law, culture, size and nature of business firms, market maturity and structure to adherence the law, best practice, the ethical values to perform HR role (Edwards & Wolfe, 2005; Interligi, 2010; Rossi, 2010). Thus, we can conclude that the HRC is an important branch of human resources to leverage and conform the HR functions, process adherences to the need to the state, and also guided by labor law as well as relevant employment laws of the country.
2. Importance of HR Compliance
As the days are going on, the importance of HR compliance is moving very faster. In addition to getting academic focus, this is now a very wider field of practices among employers, employees, and stakeholders. Over time the scope exponentially growing because of opening new departments, branches to protect the interest of the stakeholders by the business organizations. Besides, to achieve the compliance needs every firm must comply with the relevant rules, regulations and the human resources managers, professionals of the field should be aware of the compliance matters. Jensen (2015) stated that the new corporate compliance adopted by ISO in the year 2014 has created the urge of integrating HRC in business firms.
years, there are many types of research has conducted in Bangladesh. Most of the research has underscored the importance. For example, Baral (2010) has revealed that the profit of compliance industries is double that of non-compliances. Similarly, few other research claimed the importance of maintaining the standard by conforming to the HR compliances which is one of the key stimulators of today’s business (Mustapha et al., 2020). In the background, HR compliance becomes a table of discussion immediately after the pathetic fire of Tazreen Fashion and the collapse of Rana garments (Alam et al., 2017) though the government has enacted labor law in the year 2006. Likewise, many scholars have opined that the negligence of following labor law is the source of many tragic incidences in the RMG sector that accumulated the loss of quota, GSP after the incident of Rana Plaza collapse.
Conversely, many researchers have also criticized the implication of labor law, the ignorance, and management unwillingness that turned the HR issues backward in RMG (Barua et al., 2018; Chowdhury et al., 2012; Islam & Rahman, 2015; Sattar, 2018). Importantly, the key requirement of HR compliance is detailed by the labor law and in some cases some guidelines of ILO though there are given a checklist of compliance many recognized bodies of RMG buyer. Moreover, the need for decent work and workplace, the implementation code of conducts or SOP of respective principal customers, the development of periodic corrective action plan has made the strong presence of HRC. HRM compliance is essential both for employees and organization and the benefits of compliance are discussed next.
- To confirm that all human resources policies and procedures are adequately placed.
- To make sure that employees are complete and clearly aware of their work safety, security and interest related to the organizations.
- To guide the industry owners to maintain a reciprocal understanding between the employee, employer and relevant stakeholder.
- To confirm that the human resources management obligation of the organizations is adequately met.
- To safeguards the rights and interest of both employer and employee
- To keep a workplace harmony and employee motivations.
- To aware of the employer-employees charter of duties and become a standard in the industry.
- To educate the overall interest of the stakeholder for complying the laws.
3. The Scope of HR Compliances
The scope of HRC is mostly lying with the responsibility of the human resources department. Recently, many organizations were created new departments or a new section under the human resources department. For this reason, HR managers need to know the relevant matters, functional insights of HRC. This exploration showed a growing trend in HR compliance at the operational level (Mahmud & Kabeer, 2003). Relevantly the operational practices, adoption of the new process, strategies, implementation of revised policies, and process based on projected changes are mainly dependent on the nature of the business, the size, and as well as the management pattern. Because of involvement at the strategic level, the HRC adoption is fully dependent on the entrepreneur, top management, and board of directors, chief executive officer, the owner, and managing director of the organization (Legge, 1995).
In many cases, the legal matters are finished by the appointed legal consultant, the legal officer but the power of attorney is the heart of employing the functions smoothly. With this point of discussion, the performance of HRC is completely not alone in the organizations rather it has an impact on the internal and external affairs of the business. The latest development of HRC practices in Bangladesh is primarily RMG centric. It is primarily stimulated by the code of conduct of buyers. But HRC is also emerging in other segments of the manufacturing, trading, and service industry associated with many other fields of business (Rossi, 2010). Let us have a look at the scope of HRC practices:
such as Bangladesh Labor Law 2006 with subsequent amendments, Bangladesh Environmental Protection Law 1997, The EPZ workers Law 2014, Bangladesh National Building Code.2018.
3.2. International Organizations and Alliances
The HRC is directed under the guidance of many different international bodies such as International Labor Organizations, International Standardized Organization, and the business alliances such as SA8000, SAI, FWF, BSCI, WRAP, JO-IN, ILO, ETI, FLA, SEDEX, GOTS, COS, ICS, GRS.
3.3. The Functional Areas of HRC
The functional areas of HRC are advocated by previous empirical research in many contexts. The chart exhibited some of the common areas in context of Bangladesh.
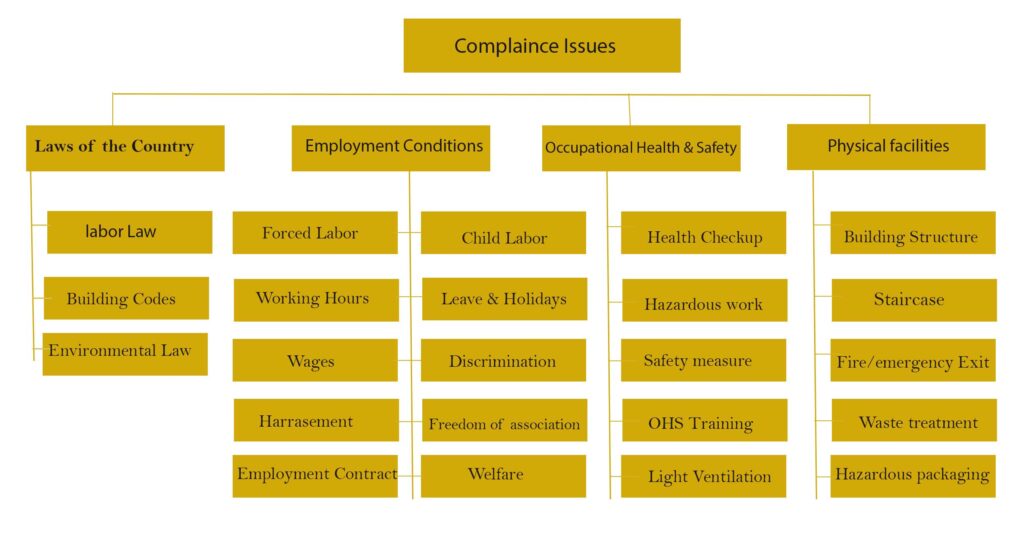
Figure 1: The operational checklist list of HR compliances adopted from (Alam et al., 2017)
4. The HR Compliances in Practices
The practices of HR compliances in gradually moving from the emerging stage to the adoption stage. The findings on the previous research in the context of Bangladesh are discussed below:
Maternity Benefits Compliance:
The eligible employees of the RMG have received the maternity benefits and leave that revealed the practices are adopted. But the findings show that the number of employees receiving benefits is not satisfactory rather limited to some specific workers. The study also revealed that the maternity leave has extended for many employees and most of them didn’t return to the job (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019). A study by Baral (2010) contented that noncompliance in the execution of maternity leave and benefits are observed in both employee and employer.
Wage Compliance:
Wages are one of the foremost areas of HRC. Previous studies in the context of Bangladesh showed that the RMG employees receive the wages in a given time but there is a shortage of their knowledge about wages payment such as overtime allowances, deductions, etc. The studies further claimed that the overtime calculation and payment are not according to the guidance of labor law.
Compensation for Injury by Accident Compliance:
The compensation of injury due to accident issues at work is a high compliance area for HR. In few studies, the result found some significant practices. For example, (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019) discovered that most of the RMG industries follow the accidental benefits and safety issues. The result further advocated that the compliance become stronger after the accident of Rana plaza but employee awareness is highly important.
Provident and Gratuity fund Compliance:
To encourage employees in long-term employment the provident fund played a significant role. The result shows that most of the large-scale garments have initialized the adoption of provident funds. But the medium and small-scale RMGs yet to focus on and adopt the provident fund provision though the labor law has prescribed the same for all RMG (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019).
Health and Hygiene Compliance:
Occupational health and safety (OHS) are also one of the influential components of HRC. Health and hygiene are also operationally significant that should not be ignored rather be underscored (Zanko & Dawson, 2012). Research in the context of RMG reflected a mix of findings all the RMG are not maintained in all areas of OHS. Research by Alam et al. (2017) shows that the knowledge and understanding of employees and factory people is one of the important causes behind OHS noncompliance. Similar research has claimed that in many RMGs the washrooms, staircases, passages, the inside walls, are not adequately cleaned through weekly cleaning is evident (Baral, 2010; Islam, 2016). On the other hand, the absence of compliance has also negatively influence employee motivation (Ansary & Barua, 2015; Mustapha et al., 2020).
Additionally, other studies evidence that the air circulation system, the temperature, the exit stair obstacles, the lack of arrow marks, the signage are not adequately set up in many RMG (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019). Besides, the drinking water system is mostly found but the lighting system was not adequate (Nurul et al., 2019). In the areas of security compliance, the result of adequate fire extinguishers, firefighting items, fire alarms were found. But the fire exits are not adequately marked or faded color (Wadud & Huda, 2017). Besides, the expiry of the cylinders is not rightly checked and the training on fire extinguisher uses not adequate though the labor law has prescribed to comply the same (Masum & Alam, 2016)
Welfare Compliance:
Since the HRC is primarily focused on the employees so welfare is one of the prime areas. In previous research, the availability of first aid box was evident in floors premise but the regular check of medicines, the total number (1 box @ 150 employees) were not found. Besides there is the availability of medical care room, child facilities but the doctors were not available on regular basis rather some selected days in a week and the child care room is not adequately cleaned rather poorly decorated. Based on labor law there is a requirement to maintain a safety record book, safety data sheet, and safety board along with formation safety committee for employee welfare. But the result of the research revealed the absence of those practices (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019).
Working Hours, Leaves and Holidays Compliance:
Working hours and related privileges are the heart of managing employees at work. Following this lead, compliance in this field is relevantly a central issue for employers. Previous studies asserted that the employees of the RMGs are availed the holidays but the compensatory holiday are not adequately encouraged. The yearly leave with pay is not rightly allowed and the sick leave is not properly practiced as per the labor law (Islam, 2016; Islam & Rakib, 2019). But in another research of ILO (2020) has supported the findings and claimed that 56% of employees cannot avail of the sick 34% cannot avail the casual leave and 20% cannot avail the festival leave. The study further claimed that 64% of employers pay overtime in due time.
Conclusion
The HRC is gradually emerging in Bangladesh. Every new beginning has underpinned with critical realities that enable modification of the process and acceptability. Indeed, HRC is the new leaves of the old tree that evolved with many advantages. The HRC is passing the hurdle of acceptability, adoption, mindset, training, organizational educations, and participation of the owners at the adoption level. Scholarly believers accept the change as an opportunity that might gradually generate holistic results instead of merely focus on profiteering. Essentially, business needs diversification and diversification require the patronization from the top level of management. The HRC is committed to producing the product that we called ‘a set standard of practice’ which would be stepping up gradually and a doctrine of the necessity of time. Thus, the outcome of HRC will not only for the organization itself rather the associated parties and group and finally the nation.
